What is a concussion?
A “concussion” is the medical term for a mild brain injury. It can cause confusion, memory loss, and headache.
A concussion usually happens after a person hits their head. But in some cases, it can happen after an injury or accident that causes violent shaking of the head.
Common causes of concussion include:
- Car accidents
- Falling down and other accidents that can happen from daily activities
- Injuries from playing sports such as football, cricket and boxing
What are the symptoms of a concussion
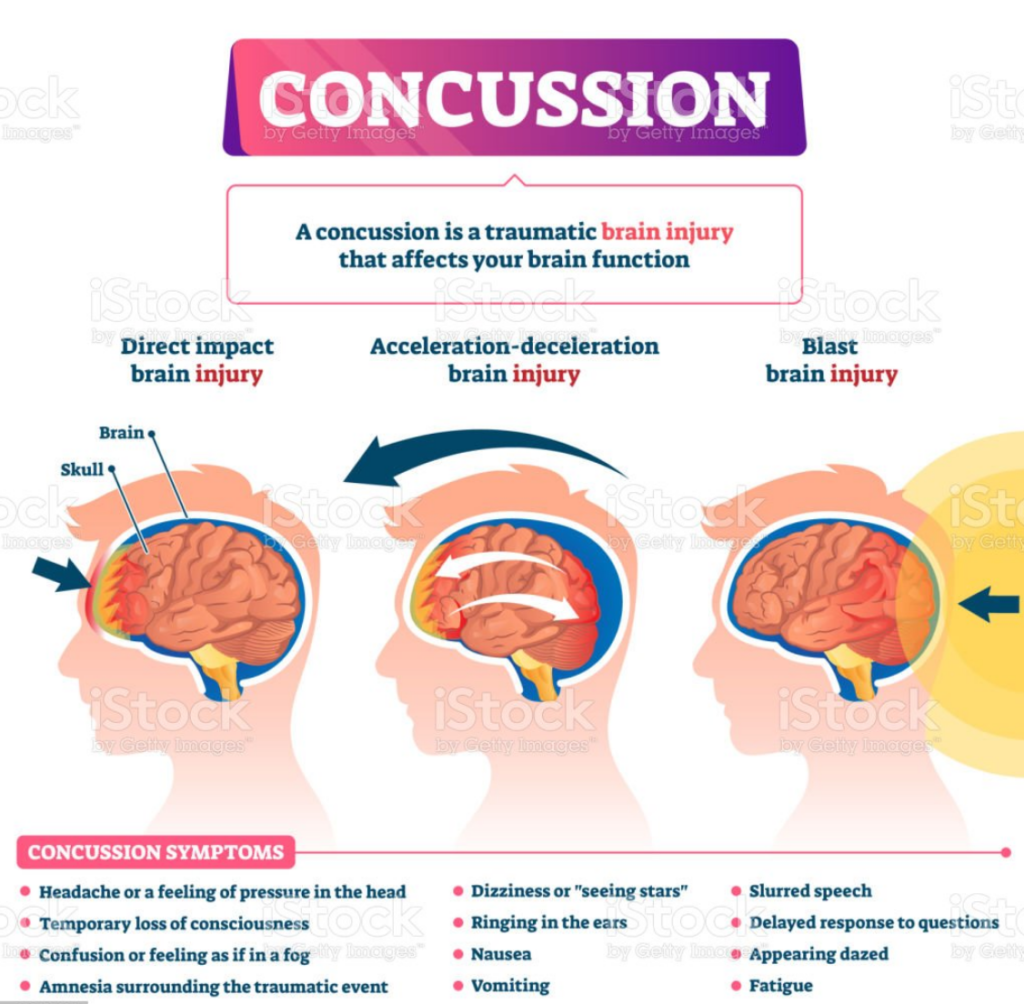
Blacking out or passing out immediately after a head injury is commonly seen in concussion.
Symptoms that can happen immediately, or in the first minutes to hours after a concussion, include:
- Memory loss – People sometimes forget what caused their injury, as well as what happened right before and after the injury
- Confusion
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dizziness or trouble with balance
Some people recover quickly from a concussion and have no further symptoms. But others have symptoms that persist or happen hours to days after a concussion. These might include:
- Trouble walking or talking
- Memory problems or problems paying attention
- Trouble sleeping or feeling very tired or sleepy
- Mood or behaviour changes (for example, acting cranky, irritable, or not like themselves)
- Being bothered by things like noise or light
Will I need tests?
It depends on your injury and symptoms. To check if you have a concussion, your doctor will ask about your symptoms and do a physical exam. They will also ask you questions to check that you are thinking clearly.
If your doctor suspects a serious injury, they might order an imaging test of the brain, such as a CT or MRI scan.
How is a concussion treated?
If you think that you are having symptoms related to a head injury or concussion, see a doctor.
Treatment of a concussion involves:
- Preventing further injury – While you are healing, it’s important not to do too much, especially activities that could lead to another head injury, like organized sports. Having a second injury while the brain is healing from a concussion can seriously damage the brain.
- Physical rest – Rest your body, and get plenty of sleep. Avoid heavy exercise or too much physical activity if it makes you feel worse.
- Mental rest – Doctors also call this “cognitive rest.” Avoid doing activities that need concentration or a lot of attention if they make you feel worse. Sometimes, activities using screens, especially video games, can make people feel worse after a concussion. You can start doing these things again as you get better
- Avoiding alcohol and cannabis while you are still having symptoms of concussion
- Treating headache – You can take an over-the-counter pain reliever if you have a headache.
Most concussions get better on their own, but it can take time. For some people, the symptoms go away within minutes to hours. Other people have symptoms for weeks to months. When symptoms last a long time, doctors call it “postconcussion syndrome.”
How can I prevent another concussion?
To help prevent another concussion, you can:
- Wear a helmet when you ride a bike or motorcycle, or play certain sports.
- Wear a seat belt when you drive or ride in a car.
If you have had a concussion, it’s very important to try to prevent future concussions. Having many concussions might cause long-term brain damage and affect your thinking.


Pingback: How to Spot the Warning Signs of a Head Injury - neuro.org.in